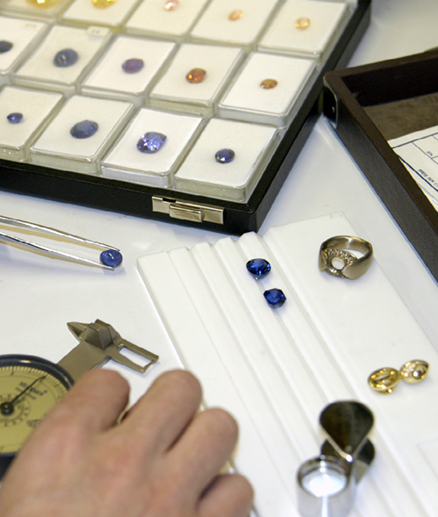
Gemmology
The science of gemstones
Gemmology is the internationally recognized science of gemstones. It is an interdisciplinary field between mineralogy, geology, physics and chemistry. The gemmologist’s task is to identify gemstones, their nature, authenticity, quality, origin and state of treatment. He must first distinguish genuine stones from synthetic stones or imitations.
Identification of gemstones
The gemmologist’s task is to identify gemstones, their nature, authenticity, quality, origin and state of treatment. He first has to distinguish genuine stones from synthetic stones or imitations. Whereas in the past the identification of synthetic stones was considered to be the most difficult job, today’s challenge is detecting the many treatments that artificially enhance a stone.
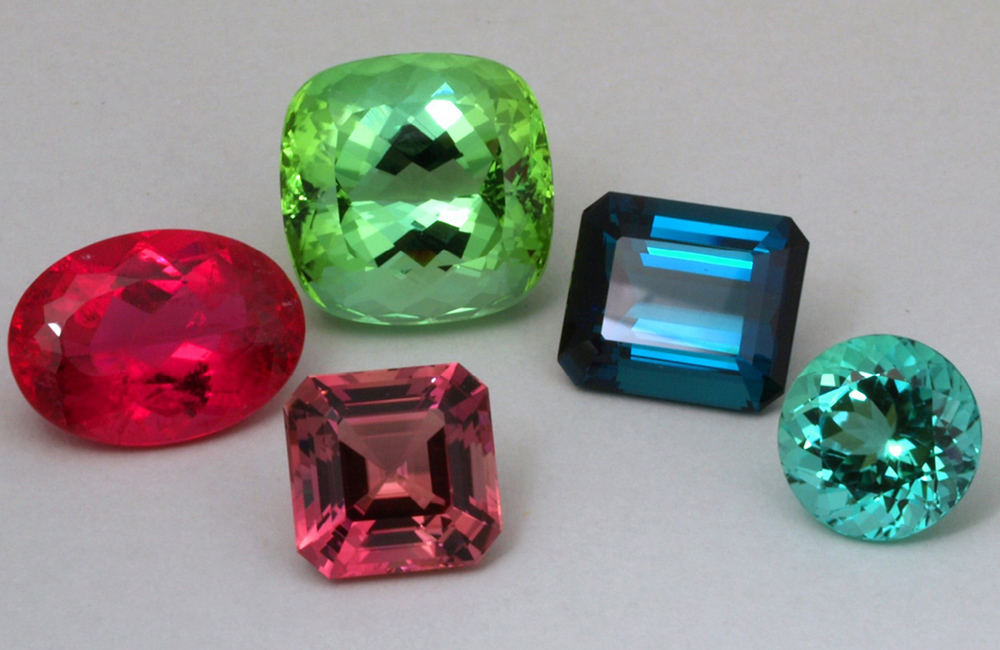

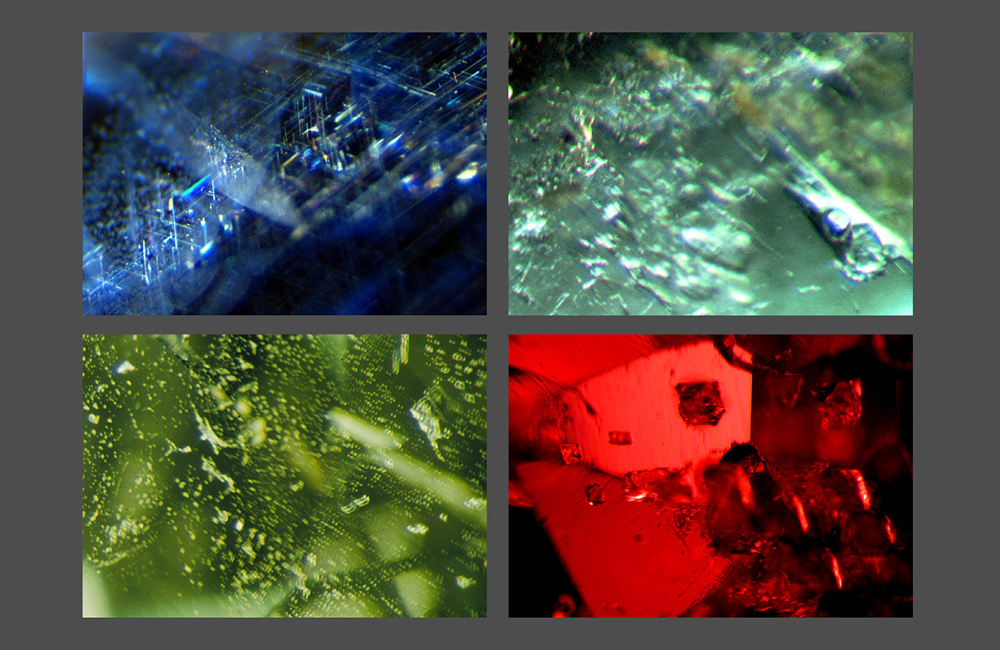
Determination of origin
An important task of the gemmologist is determining the geographical origin of the gemstone, for which comprehensive geological knowledge is necessary.
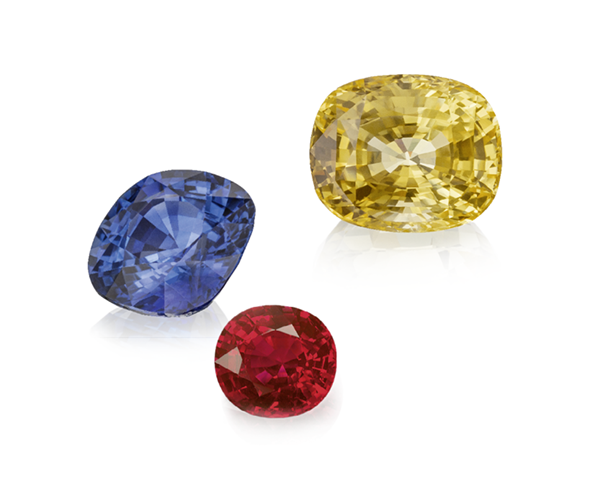
The value of coloured gemstones varies tremendously depending on their geographical origin. The most famous mines, such as those in Burma, Kashmir or Columbia, are already or will soon be depleted and high-quality gems from these deposits are becoming even more scarce.
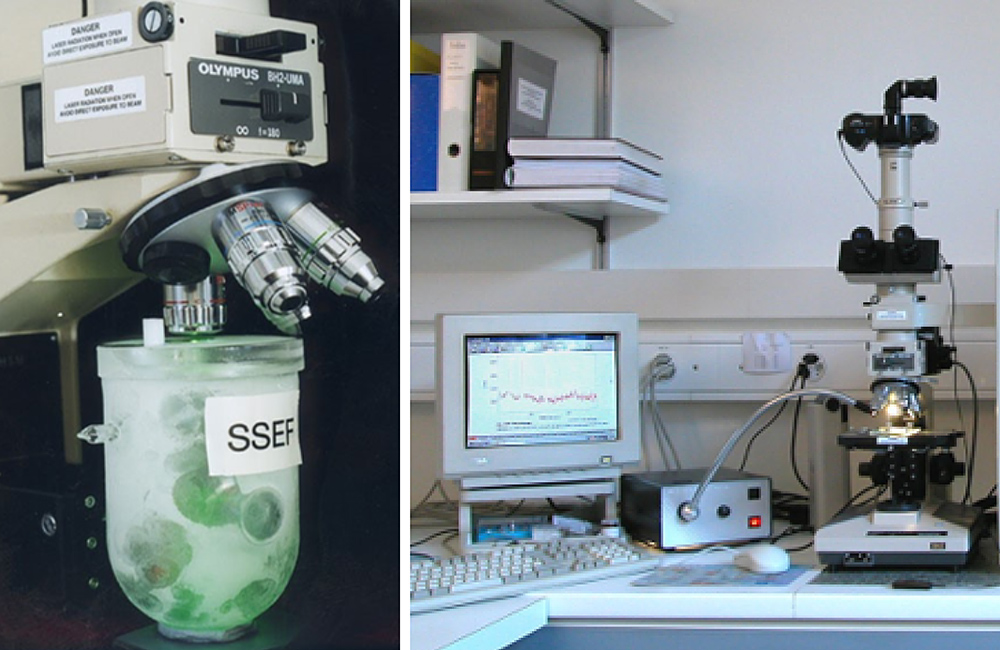
Expertise in laboratories
Determining the origin of a stone is often only possible with very expensive instruments owned by renowned gem laboratories. The SSEF (Swiss Gemmological Institute) in Basel or the Gübelin Gem Lab in Luzern are worldwide leaders in determining the origins of gemstone.


Enhancements
Today, many coloured gemstones are treated to enhance their colours. One of the main jobs of an experienced gemmologist is to detect these treatments. It is mandatory to declare all enhancements in the gemstone trade. Natural coloured gemstones are marked as having NTE (No Thermal Enhancement). These gemstones are scarce, and their prices are frequently higher than those of treated stones.
Certificates
Valuable coloured gemstones come with a certificate that confirms all of the important details of the stone, such as colour, weight, shape, cut and proportions, including proof of whether it has a natural colour (NTE) or not. Rare or valuable coloured stones have a certificate that confirms their origin. Certificates that are not issued by a known institute are meaningless. Laboratories of worldwide acclaim include: the GIA (Gemmological Institute of America) in Carlsbad California, the SSEF (Swiss Gemmological Institute) in Basel, the Gübelin in Luzern and the GRS (Gem Research Swiss Lab).






